Question of 2 marks:-
-
Can you write a class without specifying namespace? Which namespace does it belong to by default?
Answer:-
Yes, you can, and then the class belongs to global namespace which has no name. For commercial products, naturally, you wouldn’t want global namespace.
-
write down complete syntax of “getDC” function?
Answer:-
The system retrieves a device context from the cache whenever an application calls the GetDC
or BeginPaint function; the system returns the DC to the cache when the application subsequently calls the ReleaseDC or EndPaint function.
-
“In the GDI environment there are two working spaces”, Name these two.
Answer:-
In the GDI environment there are two working spaces
- Logical
- Physical
-
Message queues of each application
Answer:-
An application must remove and process messages posted to the message queues of its threads
-
A window may have more than one windows inside it explain the line
Answer:-
A Window may further contain more windows inside it. For example let’s take a calculator; A calculator contains more windows in forms of buttons, radio buttons and check boxes.
- Every Window has its parent and zero or more siblings.
- Top level window has desktop as its parent.
-
Explain Message queuing
Answer:-
Message Queue is created when every any GDI function call is made or send message or post message function calls are made. Message Queue can be attached to every thread either it is user interface thread or worker threads. User Interface threads always a message queue
-
what is stack?
Answer:-
In computer science, a stack is an area of memory that holds all local variables and parameter used by any function, and remembers the order in which functions are called so that function returns occur correctly.
-
Define “Virtual-Key” message ?
Answer:-
Virtual-key code is a device-independent value defined by the system that identifies the purpose of a key. After translating a scan code, the keyboard layout creates a message that includes the scan code, the virtual-key code, and other information about the keystroke, and then places the message in the system message queue.
-
why the entries in the parent process table and child table?
Answer:-
It means that the handle value that identifies a kernel object is identical in both the parent and the child processes
-
Define instance Handle? Briefly explain
Answer:-
This member is Application instance handle.
Question of 3 Marks:-
-
How can I use the CopyTo method of the Windows Forms controls collection to copy controls into an array?
Answer:-
The CopyTo method will take the current controls collection and copy all the controls into an array. In order to use it, you must specify the array and the starting point. For instance, the following code copies the controls to the MyArrayOfControls array starting at the first element
-
Write a complete syantax of “Getparents” functions? What kind of value it return and when this function is use?
-
How Windows keep track of the files?
Answer:-
The system requires instance handles to keep track of all modules. The system assigns a handle to each copy of a running executable or .dll.
-
How many kinds of macros are there?
Answer:-
There are two kinds of macros.
- Object-like macros resemble data objects when used,
- Function-like macros resemble function calls.
-
Paint function usage
Answer:-
Paint function performs following tasks.
- The BeginPaint() function prepares the specified window for painting and fills a PAINTSTRUCT structure with information about the painting.
- BeginPaint() first erases the background of window’s client area by sending WM_ERASEBKGND message.
- If the function succeeds, the return value is the handle to a display device context for the specified window.
-
What happened if GetUpdateWn returns zero
Answer:-
If GetUpdateRect returns zero, the application should not call the BeginPaint and EndPaint
functions.
-
What is the function of ws_paint in Windows class
Answer:-
DispatchMessage function to a window procedure when the application obtains a WM_PAINT message from message Queue by using the GetMessage or PeekMessage functions.
-
Kernel tasks 3marks
Answer:-
Kernel is a main module of the operating system. This provides system services for managing threads, memory, and resources.
Kernel has to perform very important responsibilities e.g.
- Process Management
- File Management
- Memory Management (System and Virtual Memory)
-
Infinite recursion
Answer:-
Infinite recursion, a special case of an infinite loop that is caused by recursion. This revised function will only run out of stack space if n is less than 1 or n is too large; error checking would remove the first case. For information on recursive functions which never run out of stack
-
What is extern storage class?
Answer:-
Extern defines a global variable that is visible to all object modules. When you use ‘extern’ the variable cannot be initialized as all it does is to point the variable name at a storage location that has been previously defined
-
An application can set up for itself any logical coordinates system, using API. Write down any two.
Answer:-
There are two types of brushes: logical and physical. A logical brush is one that you define in code as the ideal combination of colors and/or pattern that an application should use to paint shapes. A physical brush is one that a device driver creates, which is based on your logical-brush definition.
-
Differentiate between Super Classing and Sub Classing.
Answer:-
SuperClassing |
SubClassing |
| Super-classing defines a class that adds new functionality to a predefined window class, | Subclassing is allowed only within a process. |
| Button or list box controls. | Win32 processes have separate address spaces |
| Superclassing involves creating a new class that uses the window procedure of an existing class for basic functionality. | An application cannot subclass a window or class that belongs to another process. |
-
Write at least two tasks performed by BeginPaint () function?
Answer:-
1 The BeginPaint() function prepares the specified window for painting and fills a PAINTSTRUCT structure with information about the painting.
2 BeginPaint() first erases the background of window’s client area by sending WM_ERASEBKGND message.
-
Clipboard Working
Answer:-
In Windows, data is shareable among applications. We can use it for copying the data from one file to the other in same format.e.g from notepad to MS Word.. All the text or image data you have previously copied can now be pasted in other application.
Question of 5 marks:-
-
Differentiate pen &brush?
Answer:-
PEN |
Brush |
| A pen is a graphics tool that an application for Microsoft Windows uses to draw lines and curves | A brush is a graphics tool that a Windows based application uses to paint the interior of polygons, ellipses, and paths |
| Pens to draw freehand lines, straight lines, and curves. | brushes use to paint shapes |
| pens to designate trends in graphs and to outline bar graphs and pie charts | Brushes to paint the sections of pie charts and the bars in bar graphs. |
-
It is sometimes more efficient for an application to draw directly in a window without relying on the WM_PAINT message. How this task can be accomplished (i.e. how can we draw in a window directly without using WM_PAINT message)?
Answer:-
The task can be accomplished which is given below:-
This can be useful when the user needs immediate feedback, such as when selecting text and dragging or sizing an object. In such cases, the application usually draws while processing keyboard or mouse messages.
To draw in a window without using a WM_PAINT message, the application uses the GetDC or GetDCEx function to retrieve a display device context for the window. With the display device context, the application can draw in the window and avoid intruding into other windows. When the application has finished drawing, it calls the ReleaseDC function to release the display device context for use by other applications. application draws a selection and an intervening WM_PAINT message occurs, the application must ensure that any drawing done during the message does not corrupt the selection. To avoid this, many applications remove the selection, carry out usual drawing operations, and then restore the selection when drawing is complete
-
What are the GDI environment working space names?
Answer:-
In the GDI environment there are two working spaces
- Logical
- Physical
-
List down three Pre-Defined GDI objects in window
Answer:-
Pre-defined GDI objects in Windows are:
- Pens
- Brushes
- Fonts
- Palettes
-
What are macros and its types? Explain it with example.
Answer:-
There are two kinds of macros.
1 Object-like macros resemble data objects when used,
2 Function-like macros resemble function calls.
Example:-
Here’s a macro that computes the maximum of two numeric values:
#define min(X, Y) ((X)>(Y) ? (X)
LY))
Explain
To define a macro that takes arguments, you use the #define command with a list of parameters in parentheses after the name of the macro. The parameters may be any valid C identifiers separated by commas at the top level (that is, commas that aren’t within parentheses) and, optionally, by white-space characters. The left parenthesis must follow the macro name immediately, with no space in between
-
What is a process?
Answer:-
A series of actions or steps taken to achieve an end, a process is a collection of interrelated work tasks initiated in response to an event that achieves a specific result for the customer of the process.
-
briefly defines Modal Loop?
Answer:-
Modal loop is run by Modal dialogs and process message as does application message loop. That’s why program execution is transfer to modal loop so the modal loop itself gets messages and dispatch message.
-
Write windows Programming control process?
Answer:-
1 Edit Control
2 Static Control
-
Explain Pointer to Constant, and constant to Painter?
Answer:-
Constant pointer to variable data:
char * const ptr = buff. // constant pointer to variable data
*ptr = ‘a’;
ptr = buff2; // it will be an error
since we have declared ptr as a “constant pointer to variable data”, so we can change the contents of the place where ptr is pointing at, i.e. data but being a constant variable, the ptr value i.e. the address it contains cannot be modified.
Variable pointer to Constant data:
const char * ptr = buff. //variable pointer to constant data
*ptr = ‘a’; // it will be an error
ptr = buf2;
-
Write the complete syntax or “get parent function”
Answer:-
GetParent function returns the parent handle of the specified child. This function will be useful when the parent of the child window to use.
Syntax::
HWND GetParent
(
HWND hWnd // handle to child window
);
-
Types of assertion and name them?
Answer:-
There are three types of assertion:
1
Preconditions
- Specify conditions at the start of a function.
2
Post conditions
- Specify conditions at the end of a function.
3
Invariants
- Specify conditions over a defined region of a program
-
Write the characteristics of child windows?
Answer:-
Following are the characteristics of child windows.
- A child window always appears within the client area of its parent window.
- Child windows are most often as controls.
- A child window sends WM_COMMAND notification messages to its parent window.
- When a child window is created a unique identifier for that window is specified in hMenu parameter of CreateWindow()
-
what will happen if GetUpdateRect returns zero?
Answer:-
An application should call the GetUpdateRect function to determine whether the window has an update region. If GetUpdateRect returns zero, the application should not call the BeginPaint and EndPaint functions.
-
Define Client area?
Answer:-
The client area is the part of a window where the application displays output, such as text or graphics. For example, a desktop publishing application displays the current page of a document in the client area. The application must provide a function, called a window procedure, to process input to the window and display output in the client area.
-
WIN MAIN describe with detail
Answer:-
WinMain is the starting point in Every Win32 GUI programs. WinMain has four
Parameters these are,
- First is instance of the current application.
- Second parameter is also an instance of this application which is used for the previous application of the same type that is already running. It is used only in Window 16bit editions or Windows 3.1. Windows 32bit editions do not support this parameter. It is here just for compatibility.
- Third parameter is a command line argument of string type which is a type defined as char *.
- Fourth parameter is windows style.
-
Differentiate
Desktop Window and Application Window
Answer:-
Desktop Windows |
Application Windows |
| When you start the system, it automatically creates the desktop window. The desktop window is a system-defined window | When you start an application, the system also associates a taskbar button with the application. The taskbar button contains the program icon and title |
| uses a bitmap to paint the background of the screen | Most applications also create other windows, either directly or indirectly, to perform tasks related to the main window |
| A system configuration application, such as a Control Panel item, changes the desktop wallpaper by using the System Parameters Info function | An application window includes elements such as a title bar, a menu bar, the window menu (formerly known as the system menu), |
-
show the implementation of _cdecl calling convolution with respect to
Answer:-
1: Argument passing order.
2: stack maintenance responsibility.
3: name decoration convention.
-
Difference between __stdcall and __cdecl calling convention
Answer:-
cdecl and __stdcall just tells the compiler whether the called function or the calling function
cleans up the stack. In __stdcall calling convention, the called function cleans up the stack when
it is about to return. So if it is called in a bunch of different places, all of those calls do not need
to extra code to clean up the stack after the function call.
In __cdecl calling convention, it is the caller function that is responsible for cleaning the stack,
so every function call must also need to include extra code to clean up the stack after the
function call.
-
Erase window function explanation
Answer:-
Erase windows uses the GetClipBox function to retrieve the logical coordinates of the area to erase and passes these coordinates to the FillRect function. Applications that process these messages can use similar techniques. The system supplies a window device context with the WM_ICONERASEBKGND message regardless of whether the corresponding window has a private device context.
-
what happened if an application does not process WM_ErasebkGrd massages but pass it defWindowProcs.
Answer:-
If it processes
WM_ERASEBKGND
, the application should use the message’s wParam parameter to draw the background. This parameter contains a handle to the display device context for the window. After drawing the background, the application should return a nonzero value. This ensures that
BeginPaint
does not erroneously set the
fErase
member of the
PAINTSTRUCT
structure to a nonzero value (indicating the background should be erased) when the application processes the subsequent
WM_PAINT
message.
An application can define a class background brush by assigning a brush handle or a system color value to the
hbrBackground
member of the
WNDCLASS
structure when registering the class with the
RegisterClass
function. The
GetStockObject
or
CreateSolidBrush
function can be used to create a brush handle. A system color value can be one of those defined for the
SetSysColors
function. (The value must be increased by one before it is assigned to the member.)
-
List down the important distance between subclassing and superclassing?
Answer:-
SuperClassing |
SubClassing |
| Super-classing defines a class that adds new functionality to a predefined window class, | Subclassing is allowed only within a process. |
| Button or list box controls. | Win32 processes have separate address spaces |
| Superclassing involves creating a new class that uses the window procedure of an existing class for basic functionality. | An application cannot subclass a window or class that belongs to another process. |
-
Write down the code c/c++ program that has 2 functions on take 4 integer variable as parameters and return their sum and other take 4 integer as arguments and return their multiplication.
Answer
#include <stdio.h>
// prototypes, the parameter names are optional,
// print the menu and obtains a selection
int GetChoice();
// inserts a number in the sorted array.
int AddNum (int num[], int sz);
// removes a number from the array.
int DelNum(int num[], int sz);
// prints out the sorted array
void PrintNums(int num[], int sz);
void main()
{
// the number of elements in array A[]
int Size = 0,
// the array that will keep its numbers sorted
A[20],
// the selection made from the menu
Selection;
// keep doing this loop until a 4 or Quit is
// selected from the menu…
Selection = GetChoice();
for( ; Selection != 4; )
{
if(Selection == 1)
Size = AddNum(A, Size);
else
if(Selection == 2)
Size = DelNum(A, Size);
else
PrintNums(A, Size);
Selection = GetChoice();
}
}
// assuming that user will enter only a valid int
int GetChoice()
{
int Choice;
printf(“Enter 1 – Insert, 2 – Delete, “);
printf(“3 – List and 4 – Quit: “);
scanf_s(“%d”, &Choice);
return Choice;
}
int AddNum(int Num[ ], int sz)
{
// local variables…
int i, j, Number;
// gets the number to insert
printf(“What number to insert? “);
scanf_s(“%d”, &Number);
// finds the place (i) to put the new number
for(i = 0; i < sz; ++i)
if(Number < Num[i])
break;
// shift the rest of the array by moving
// the numbers up by one slot.
for(j = sz; j > i; –j)
Num[j] = Num[j – 1];
// place the new number
Num[i] = Number;
// the array size is incremented
// and return to the calling function
return ++sz;
}
// assuming that the deleted item exists
int DelNum(int Num[], int sz)
{
// local variables…
int i, Number;
// gets the number to be deleted
printf(“What number are you going to delete? “);
scanf_s(“%d”, &Number);
// find the place in the array to be deleted
for(i = 0; i < sz; ++i)
if(Number == Num[i])
break;
// the array size is decremented
–sz;
// shift the rest of the array by moving the numbers
// down by one slot
for( ; i < sz; ++i)
Num[i] = Num[i + 1];
// return sz to the calling function
return sz;
}
void PrintNums(int Num[ ], int sz)
{
// local variable…
int i;
for(i = 0; i < sz; ++i)
printf(“Num[%d] = %d\t”, i, Num[i]);
printf(“\n”);
}
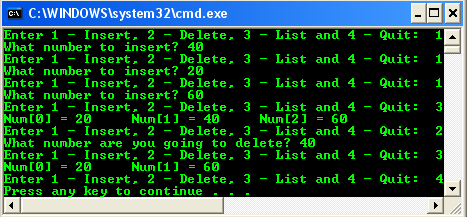
Output of this Program
-
Write two macros that perform the same tasks as these functions perform?
Answer:-
A macro is a fragment of code which has been given a name. Whenever the name is used, it is replaced by the contents of the macro. There are two kinds of macros. They differ mostly in what they look like when they are used. Object-like macros resemble data objects when used, function-like macros resemble function calls.
You may define any valid identifier as a macro, even if it is a C keyword. The preprocessor does not know anything about keywords. This can be useful if you wish to hide a keyword such as const from an older compiler that does not understand it. However, the preprocessor operator defined can never be defined as a macro, and C++’s named operators cannot be macros when you are compiling C++.
To define a macro that takes arguments, you use the #define command with a list of parameters in parentheses after the name of the macro. The parameters may be any valid C identifiers separated by commas at the top level (that is, commas that aren’t within parentheses) and, optionally, by white-space characters. The left parenthesis must follow the macro name immediately, with no space in between.
For example, here’s a macro that computes the maximum of two numeric values:
#define min(X, Y) ((X)>(Y) ? (X):(Y))
-
Two common controls in window programming
Answer:-
Common controls are of these types.
- Date Time Picker Control.
- List View Control.
-
About _cdecl calling convention?
Answer:-
The __cdecl is the default calling convention for C programs. In this calling convention, the stack is cleaned up by the caller. The __cdecl calling convention creates larger executables than __stdcall, because it requires each function call to include stack cleanup code.
CS410 Solved Subjective Mega Collection for Mid term papers Click here to Download