Problem Statement: Location Calculation
You are required to write a program for calculating location somewhere on the map. There are two parameters (coordinates) used in calculating a location. One is longitude and the other is latitude. You need to overload ++, –, new and delete operators for this.
Detailed Description:
You are required to create a class named Location.
It will have two private data member longitude and latitude.
These data members will be assigned values through constructor parameters. For example obj1(20,30).
Overloaded ++ operator will increase the both longitude and latitude values by one, overloaded — will decrease both by one.
By overloading new operator, you will allocate the memory dynamically for the object of class Location.
The overloaded delete operator will free (de-allocate) the allocated memory.
You have to create two objects of class Location. One object will be created through overloaded new operator and other will be created without it.
A message “Overloaded new operator called”, embedded inside overloading function for new operator, should be displayed when the object is created through new operator.
Similarly, a message “Overload delete operator called” should be displayed upon calling overloaded function of delete operator.
Assign the values (10, 20) and (30, 40) for longitude and latitude for object 1 and 2 respectively.
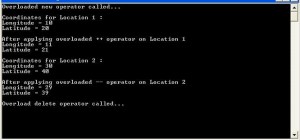
Sample Output:
/****************** Assignment No. 4 : Solution **********************\
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <conio.h>
using namespace std;
class Location {
int longitude, latitude;
public:
Location() {}
// parameterized constructor
Location(int lg, int lt) {
longitude = lg;
latitude = lt;
}
void show() {
cout << “Longitude = ” <<longitude << endl;
cout << “Latitude = ” <<latitude << “\n”;
}
void *operator new(size_t size); //overloaded new operator receive a parameter size of size_t
void operator delete(void *p);
Location operator–(int x);
Location operator++(int x);
};
// new overloaded relative to loc.
void *Location::operator new(size_t size)
{
void *p;
cout << “Overloaded new operator called…\n”;
p = malloc(size); // allocate memory through alloc
return p; // return the position
}
// delete overloaded relative to loc.
void Location::operator delete(void *p)
{
cout << “Overload delete operator called…\n”;
free(p); // free the allocatated position
}
// — overloaded
Location Location::operator–(int x)
{
longitude–; // decrement the longitude
latitude–; // decrement the latitude
return *this;
}
// ++ overloaded
Location Location::operator++(int x)
{
longitude++; // increment the longitude
latitude++; // increment the latitude
return *this;
}
int main()
{
Location *p1 = new Location (10, 20);
cout<< endl <<“Coordinates for Location 1 :” << endl;
p1->show();
cout<< endl <<“After applying overloaded ++ operator on Location 1″<<endl;
(*p1)++;
p1->show();
Location p2(30, 40);
cout<< endl <<“Coordinates for Location 2 :” << endl;
p2.show();
cout<< endl <<“After applying overloaded — operator on Location 2″<<endl;
p2–;
p2.show();
cout << endl;
delete p1; // free the memory
getch();
return 0;
}
Download the Solution file From Here